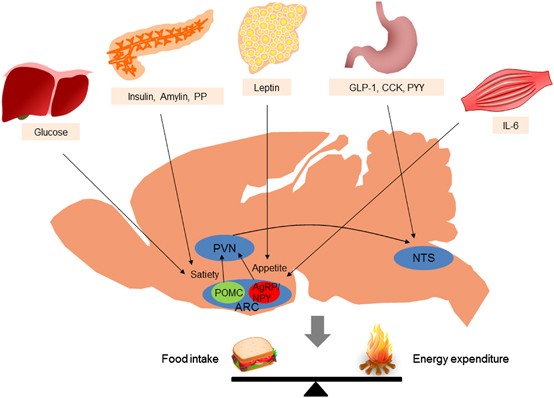
Emerging role of the brain in the homeostatic regulation of energy and glucose metabolism | Experimental & Molecular Medicine

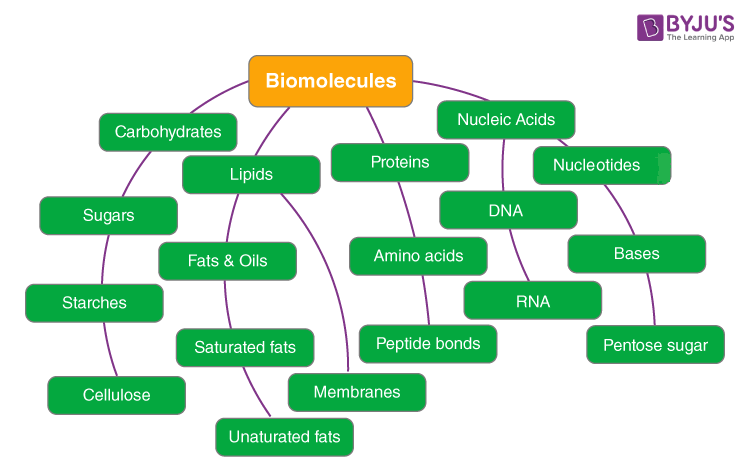
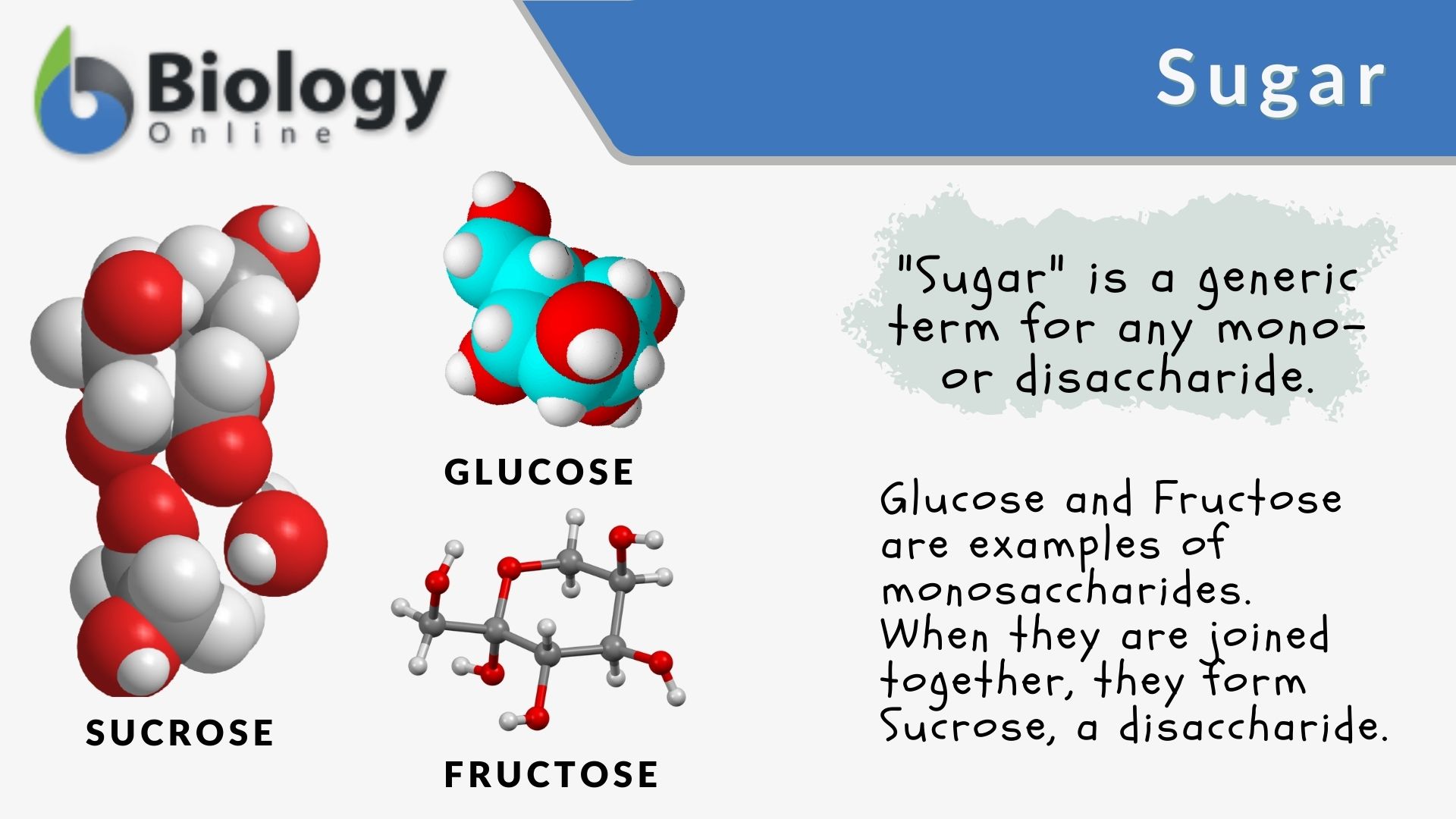
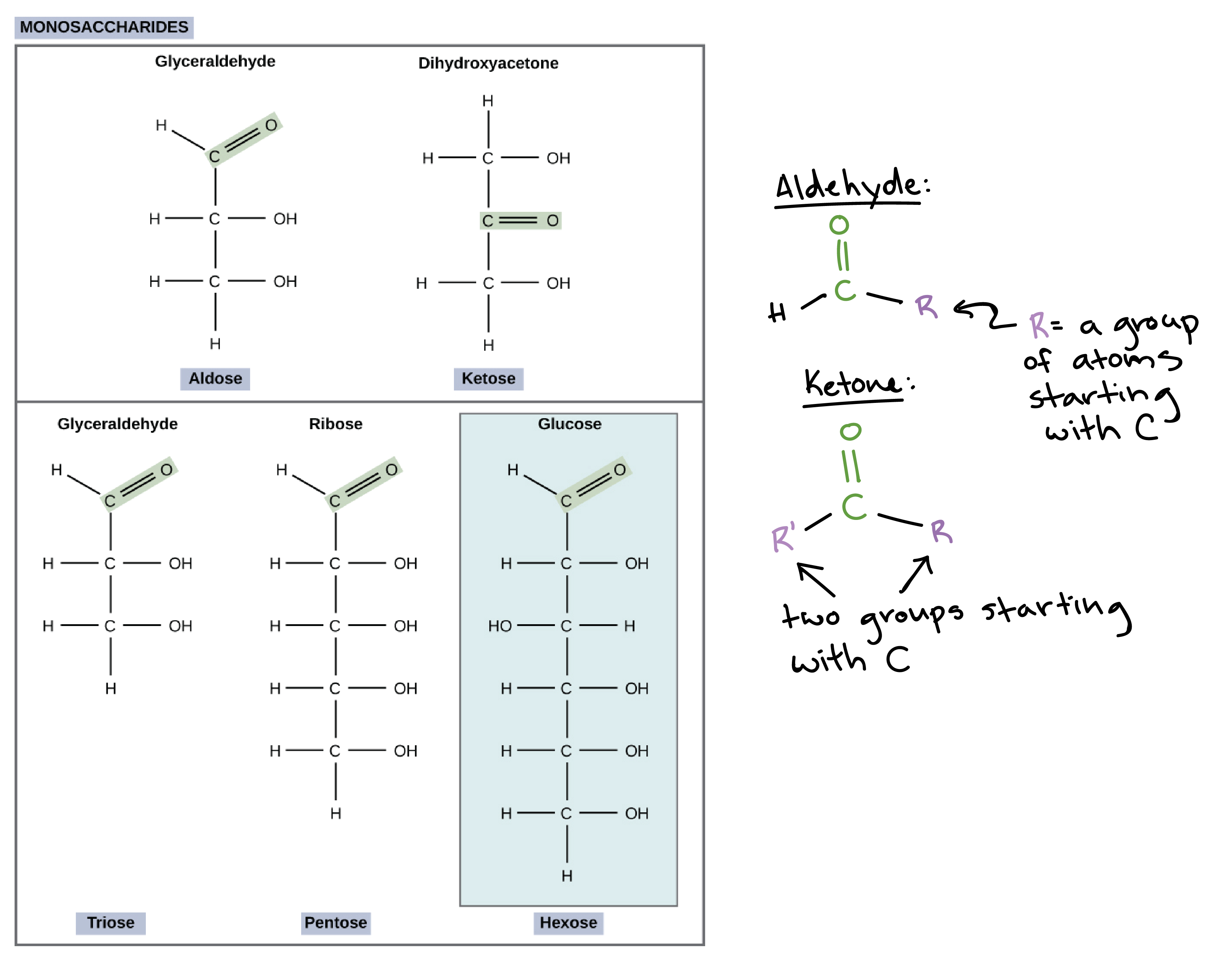
Carbohydrates Review. Carbohydrates 1. What is a Carbohydrate? A carbohydrate is any of the group of organic compounds consisting carbon, hydrogen, and. - ppt download
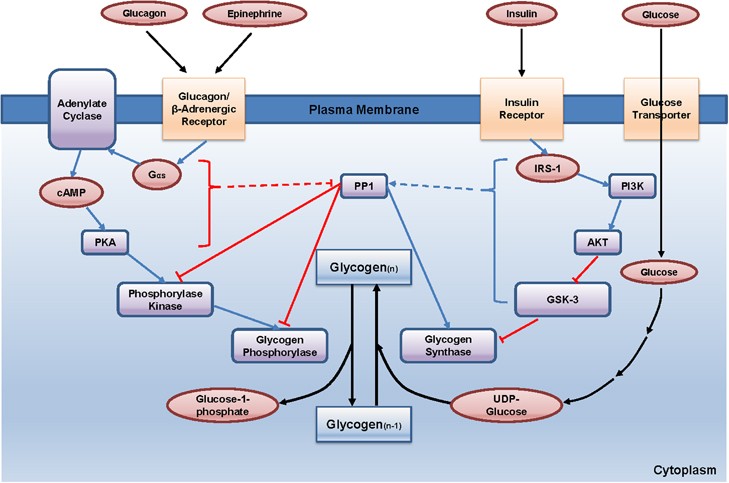
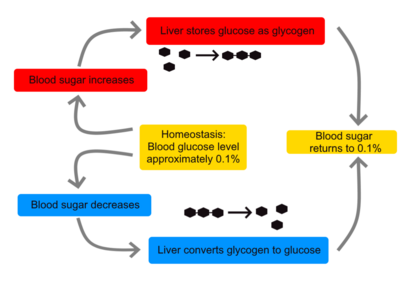
Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective | Experimental & Molecular Medicine
![PDF] Rethinking the role of the brain in glucose homeostasis and diabetes pathogenesis. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Rethinking the role of the brain in glucose homeostasis and diabetes pathogenesis. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/534644ca6fad8dc67276b1ac9347eb8af477f4fa/3-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Rethinking the role of the brain in glucose homeostasis and diabetes pathogenesis. | Semantic Scholar

Cellular Respiration Purpose: Create ATP molecules from Glucose!Purpose: Create ATP molecules from Glucose! Who uses this? ALL LIVING ORGANISMS.Who uses. - ppt download






![The Functions of Carbohydrates in the Body – Human Nutrition [DEPRECATED] The Functions of Carbohydrates in the Body – Human Nutrition [DEPRECATED]](https://pressbooks-dev.oer.hawaii.edu/humannutrition/wp-content/uploads/sites/10/2017/11/image7-1.jpg)